How to Find Long Tail Keywords

Finding long tail keywords for your blog post involves a combination of research, creativity, and understanding your target audience. Long-tail keywords are longer and more specific keyword phrases that typically have lower search volume but can bring in highly targeted and engaged traffic to your blog. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you find relevant long-tail keywords for your blog post:
Understand Your Audience:
Define your target audience and understand their needs, preferences, and pain points. This will help you generate keywords that are relevant to their interests.
Brainstorm Seed Keywords:
Start with a few general keywords that are related to your blog post topic. These will serve as your starting point for generating long-tail keywords. For example, if your blog post is about “healthy smoothie recipes,” your seed keyword could be “smoothie recipes.”
Use Keyword Research Tools:
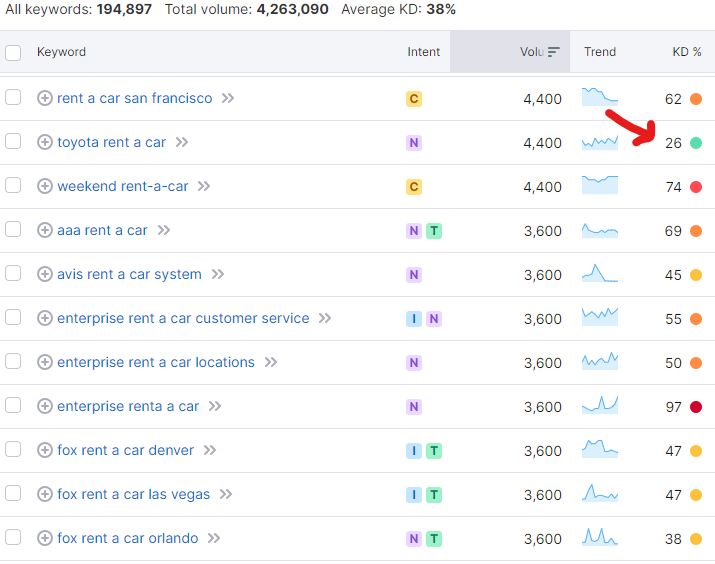
Utilize keyword research tools to expand your seed keywords into long-tail variations. Some popular tools include:
Explore Autocomplete Suggestions:
When you start typing a keyword into a search engine (like Google), it suggests autocompletions based on popular searches. These suggestions can provide insights into long-tail variations. For instance, typing “smoothie recipes for…” might lead to suggestions like “smoothie recipes for weight loss,” “smoothie recipes for kids,” etc.
Analyze Related Searches:
At the bottom of the search engine results page, you’ll find a section called “People also ask” or “Related searches.” These are great sources for generating long-tail keywords that people are actively searching for.
Check Out Competitor Content:
Analyze blog posts and content from competitors in your niche. Look for the keywords they are targeting and consider similar or related long-tail keywords that you could use.
Consider User Intent:
Focus on understanding the intent behind each keyword. Are users looking for information, solutions, products, or comparisons? This will help you create content that aligns with user expectations.
Long-Tail Keyword Variations:
Build variations of your seed keywords by adding specific details. For instance, “low-calorie smoothie recipes,” “fruit-based smoothie recipes,” “vegan smoothie recipes,” etc.
Use Question Keywords:
Incorporate question-based long-tail keywords like “how to make healthy smoothies,” “what are the benefits of smoothies,” etc. These phrases often reflect user queries.
Leverage Location and Context:
If applicable, add location-specific or contextual keywords. For example, “best smoothie recipes for summer,” “smoothie recipes using local fruits,” etc.
Prioritize Relevance and Search Volume:
While long-tail keywords have lower search volumes, prioritize those that are relevant to your content and have a reasonable amount of search traffic. It’s better to rank well for a specific, relevant keyword than to rank poorly for a high-volume but unrelated keyword.
Organize Keywords:
Once you’ve generated a list of long-tail keywords, organize them by relevance and intent. You can use spreadsheets or keyword research tools to keep track of your findings.
Implement in Content:
Integrate these long-tail keywords naturally into your blog post’s title, headings, subheadings, and throughout the content. Ensure that your content remains high-quality and valuable to readers.
Remember that the goal of using long-tail keywords is to attract a smaller, but more engaged and relevant audience. This can lead to higher conversion rates and a more targeted readership for your blog post.
What is keyword difficulty?
Keyword difficulty (KD) is a metric used in search engine optimization (SEO) to assess how challenging it would be to rank a specific keyword or keyphrase on search engine results pages (SERPs). In other words, keyword difficulty indicates the level of competition you’ll face when trying to achieve a high ranking for a particular keyword.
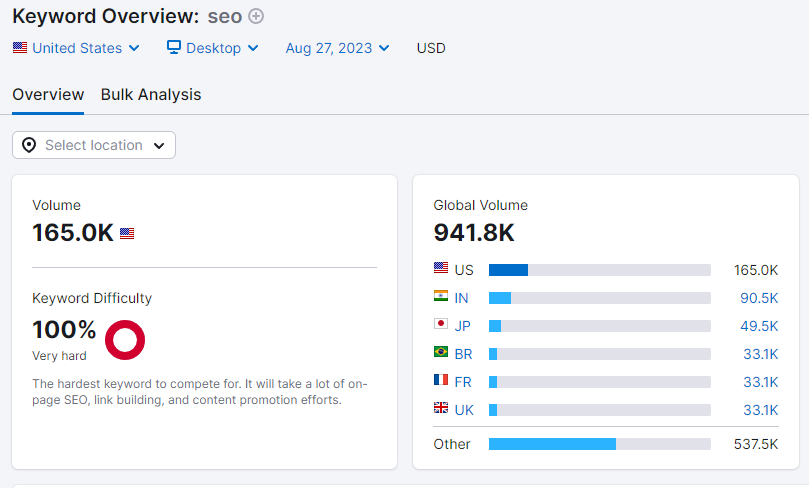
Keyword difficulty is typically measured on a scale, often from 0 to 100, where higher values indicate greater difficulty. Here’s how it generally works:
- Low Keyword Difficulty (0-30): Keywords with low difficulty are easier to rank for because there is less competition. These keywords are often more specific or longer-tail phrases that might have lower search volumes but can be easier to target successfully.
- Medium Keyword Difficulty (31-60): Keywords with medium difficulty have a moderate level of competition. These keywords are more common and often have a balance between search volume and competition.
- High Keyword Difficulty (61-100): Keywords with high difficulty are challenging to rank for due to intense competition. These are usually very common or highly competitive keywords that many websites are targeting.
The keyword difficulty score is influenced by several factors, including:
- Authority and Backlinks: The number and quality of backlinks pointing to the top-ranking pages for the keyword. Pages with a higher number of authoritative backlinks are often harder to outrank.
- Domain Authority: The overall authority and trustworthiness of your website. Newer or less established websites might find it more difficult to rank for highly competitive keywords.
- Content Quality: The quality, relevance, and comprehensiveness of your content. Well-structured, informative content that answers user queries can improve your chances of ranking well.
- On-Page Optimization: How well your content is optimized for the target keyword, including its placement in titles, headings, meta tags, and throughout the content.
- SERP Features: The presence of special SERP features like featured snippets, knowledge panels, and video carousels can impact your ability to rank.
- Competitor Landscape: The number and strength of competitors targeting the same keyword.
Keyword difficulty is an essential factor to consider when selecting keywords to target in your SEO strategy. It’s generally recommended to target a mix of low, medium, and high difficulty keywords based on your website’s authority and your content creation capabilities. Targeting only high-difficulty keywords might lead to frustration and slow results, while focusing solely on low-difficulty keywords might not yield enough traffic. Balancing your keyword targeting can help you achieve a well-rounded and effective SEO strategy.